Wet electrostatic precipitator
Wet electrostatic precipitator technology
Principle of wet electrostatic precipitator (WESP)
Wet electrostatic precipitator is developed on the basis of overcoming the disadvantages of water jet precipitator and electrostatic precipitator. Its working principle is the same as that of ordinary precipitator. It mainly involves three basic processes: charging of suspended particles, migration and capture of charged particles in electric field, and removal of catches from the surface of the dust collector. The process is roughly as follows: the dusty gas is transported to the dust collector electric field through the air inlet and air distribution system, while the water is sprayed in a fog under the action of the nozzle, in which the nozzle is arranged above the air inlet and the electric field at the same time. At the inlet of the dust collector, the dust in the dusty gas will collide with the water mist and fall into the ash hopper in the form of particles. In the electric field area, the charged water droplets will be captured by the dust collector and fall on the dust collector plate under the action of electric field force, and the dust in the gas will also be charged after being wetted by the charged water droplets, so it will also fall on the dust collector plate. After enough water droplets are captured by the dust collector, a water film will be formed on the dust collector plate, so the captured dust will flow into the ash hopper through the flow of water film, Then it is discharged into the sedimentation tank through the ash hopper.
As shown in Figure 1, in the wet electrostatic precipitator process, the metal discharge electrode ionizes the surrounding gas under the action of DC high voltage. The dust is charged in the electric field and moves to the dust collector under the action of electric field force. When it moves to the surface of the dust collector. It is removed as the liquid film flows down. Therefore, the three stages of WESP operation are the same as that of dry ESP - charging, collection and ash removal. However, different from rapping, WESP uses liquid to wash the surface of the dust collector.
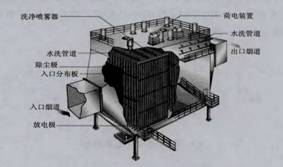
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of wet electrostatic precipitator
3 Introduction to wet electrostatic precipitator process
3.1 wet electrostatic precipitator
WESP can be divided into two basic types in terms of structure, namely tube type and plate type (as shown in Figure 2). Among them, the tubular WESP has only vertical flue gas flow (upward flow or downward flow), while the plate WESP design can adopt both horizontal flue gas flow and vertical flue gas flow. In general, tubular WESP is more efficient than plate WESP and occupies less space due to its simple shape, which has become the trend of research and application of wet electrostatic precipitator technology.
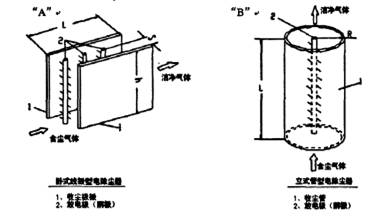
Fig. 2 two basic structural types of wet electrostatic precipitator
Other differences between the two wesps are: (1) for a given dust removal efficiency and the same electrode length, the allowable flue gas flow rate of tubular WESP is twice that of plate WESP; (2) For a given dust removal efficiency, the local drying area of tubular WESP is smaller than that of plate WESP.
The tubular WESP can be designed as either vertical upward flue gas flow or vertical downward flue gas flow. In the vertical upward flue gas flow and tubular WESP, the flue gas enters the electrostatic precipitator from the bottom and flows upward. The flushing nozzle can be placed at the bottom of the device and sprayed upward, or a downward spraying nozzle can be set above the electric field. In the vertical downward flue gas flow design, the flue gas enters the WESP from the top and flows downward. The nozzle is placed on the top and sprayed downward, and the direction is the same as the flue gas flow. In some cases, the design of downward flue gas flow will reduce the use of connecting flue, but it needs to set up a mechanical demister before the flue gas enters the chimney to capture the water mist carried with the flue gas. On the contrary, an upward flue gas flow, tubular WESP has the ability to capture submicron droplets, so it can be used as a demister with excellent performance without adding any mechanical demister.
3.2 process application of wet electrostatic precipitator
As a key process for the treatment of flue gas submicron ions, acid mist, secondary particles and other pollutants, wet electrostatic precipitator is usually combined with other treatment processes. For example, the wet electrostatic precipitator (WESP) in the process flow of the new flue gas treatment island has three process layout forms:
Process flow (I): it is composed of denitration, electrostatic precipitator, wet desulfurization and wet electrostatic precipitator. The flue gas enters the chimney after the wet electrostatic precipitator, as shown in Figure 3.
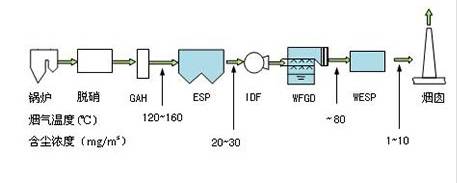
Figure 3 process flow of new flue gas treatment Island (wet electrostatic precipitator) (I)
Process flow (II):
It is composed of denitration system, low-temperature economizer waste heat utilization device + low-temperature electrostatic precipitator, wet desulfurization system and wet electrostatic precipitator. The flue gas is discharged into the chimney after passing through the wet electrostatic precipitator, as shown in Figure 4.
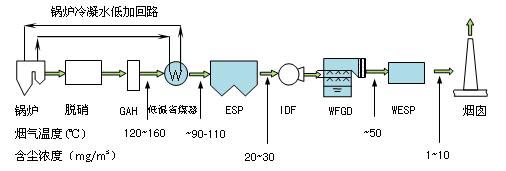
Figure 4 process flow of new flue gas treatment Island (wet electrostatic precipitator) (II)
Process flow (III): it is composed of denitration, mggh + low and low temperature electrostatic precipitator, wet desulfurization, wet electrostatic precipitator and mggh. The flue gas enters the chimney after being heated by MGG, as shown in Figure 5.
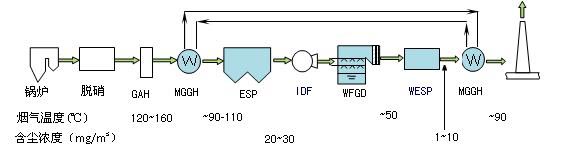
Figure 5 process flow of new flue gas treatment Island (wet electrostatic precipitator) (III)
4 development trend of wet electrostatic precipitator
China's wet electrostatic precipitator technology has developed rapidly. Since its research and development in 2009, it has achieved several engineering achievements in just a few years, and has contracts for 1000MW units of coal-fired power plants. It is ready to go, with a great potential of springing up. The successful experience of wet electrostatic precipitator in operation shows that the construction of wet electrostatic precipitator after wet desulfurization in coal-fired power plant can be used as a technical control measure at the end of the chimney to achieve ultra-low emission and comprehensively solve the problems of smoke and dust and PM2 5. Gypsum rain, SO3, mercury, various heavy metals, dioxins, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and other pollutants contribute to the control of smog.
Under the background of increasing attention to composite pollutants at home and abroad, many foreign enterprises and research institutions began to pay attention to WESP technology and made a lot of in-depth research on it. New wet ESP technologies and equipment such as wet membrane ESP, plasma enhanced ESP and dry wet composite ESP have emerged.
(1) Wet membrane electrostatic precipitator technology
The theory of membrane electrostatic precipitator was put forward by pasict of Ohio University in 1979. After years of research, scholars of the university successfully developed the membrane electrostatic precipitator and applied for a patent. The dust collector adopts conductive carbon fiber or silicon fiber woven film as the dust collector. The water flow is evenly distributed on the surface of the film through capillary action, and there will be no local dry area when collecting dust. The formation of back corona is avoided and the stability of inter electrode current is strengthened. While further improving the dust removal efficiency, it can also effectively remove harmful substances such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides and heavy metals, making it possible to realize the integration of dust removal, desulfurization and denitration in ESP at the same time.
(2) Plasma enhanced electrostatic precipitator technology
Plasma enhanced electrostatic precipitator technology is a generalized electrostatic precipitator technology with great development significance, which can simultaneously remove dust, desulfurization, denitration and purify other harmful gases. Low temperature plasma can effectively produce a variety of molecular excited states such as high-energy electrons, ions and free radicals. The dust in flue gas is charged and trapped in discharge plasma; Harmful components in flue gas such as sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, heavy metals (such as mercury) and dioxins are oxidized in plasma and absorbed by neutralizers or absorbers. So as to achieve purification. Plasma enhanced electrostatic precipitator (peesp) is a combination of electrostatic precipitator technology and low-energy plasma technology. It is a new type of mercury removal system for flue gas of coal-fired boiler. Compared with absorption mercury removal technology. This technology has the advantages of high energy efficiency and less secondary waste.
(3) Dry wet composite electrostatic precipitator technology
Combine the advantages of dry ESP and wet esp. The American Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) began to study the dry and wet composite electrostatic precipitator (dry electrostatic precipitator is used in the front stage electric field and wet electrostatic precipitator is used in the last stage electric field) in the 1990s. A series of pilot tests have been carried out since 1994, and the results show that it is effective for PM2 In 2000-2001, EPRI established a full-scale composite ESP demonstration project to reduce turbidity at Dickerson power plant in Mirant. The performance test found that it had no effect on PM2 5 and SO3, with high removal efficiency and low turbidity of 10%. In 2004, EPRI and crcat built a dry wet composite electrostatic precipitator pilot plant. The dry wet composite electrostatic precipitator technology can remove PM2 without additional activated carbon / bag technology equipment 5. Purpose of acid mist and mercury.
5 applicable fields of wet electrostatic precipitator technology
With reference to relevant application reports and technical documents of wet electrostatic precipitator, the applicable fields of technology are summarized, mainly including:
(1) Non ferrous metal smelting dust removal
(2) Acid mist treatment in sulfuric acid industry
(3) Converter gas dust removal
(4) High humidity smoke and dust in iron and steel industry
(5) Flue gas dust removal of coal-fired power plant



